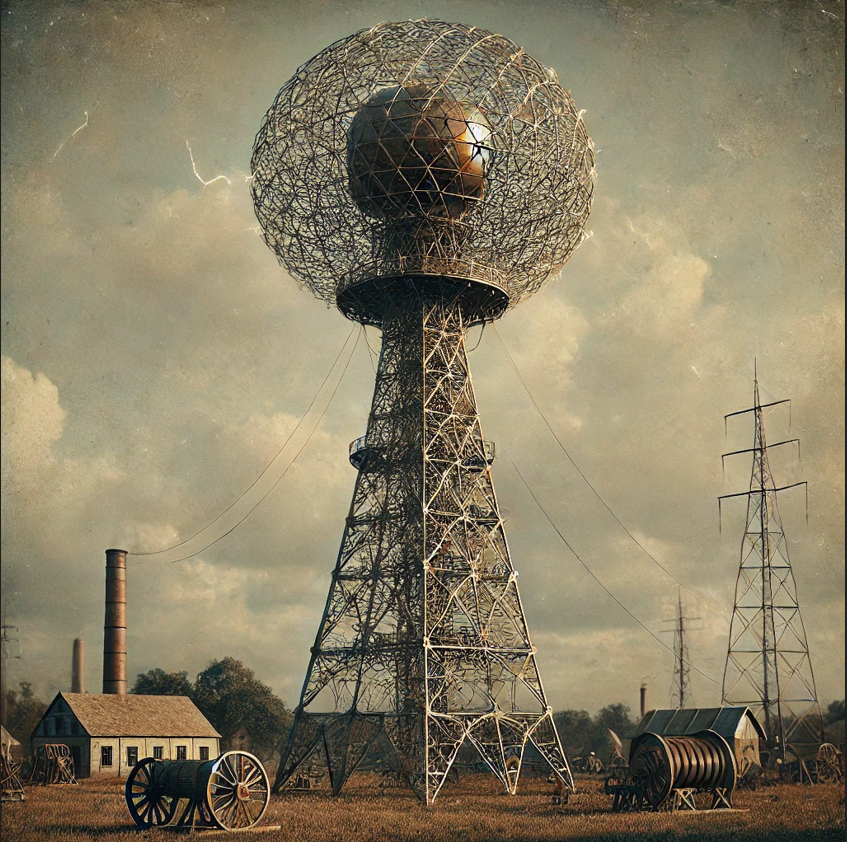
The Tesla Wireless Transmission Tower, also known as the Wardenclyffe Tower, was a project initiated by Nikola Tesla in the early 20th century to demonstrate wireless transmission of electricity. Tesla had already developed pioneering technology for alternating current (AC) and wanted to create a global wireless communication and power distribution system using this tower.
1. Location and Design
- The Wardenclyffe Tower was built in Shoreham, Long Island, New York, between 1901 and 1905.
- It was a large structure, about 187 feet tall, with a dome-shaped top that was designed to transmit signals through the earth rather than through the air, using the ground as a conductor.
- Tesla’s design used the concept of resonant frequencies—he believed that the Earth could conduct electrical signals over long distances with little energy loss.
2. Purpose and Vision
- Global Wireless Power: Tesla envisioned a system where electricity could be wirelessly transmitted around the globe, providing free energy to everyone without the need for power lines. He believed this could revolutionize industries and provide power to remote regions.
- Wireless Communication: He also planned for the tower to enable wireless communication across continents, making it possible to send messages, images, and even telephone calls wirelessly—well before the internet and modern communication systems.
3. Technical Challenges
- Tesla’s system was based on his theory that electricity could be transmitted through the Earth via low-frequency electromagnetic waves. He designed the tower to resonate with these frequencies.
- His concept of using ground-based conduction for long-distance transmission was highly unorthodox compared to modern wireless technologies that use air-based transmission (radio waves).
- The tower also incorporated ideas from his earlier experiments with high-voltage and high-frequency electrical energy (e.g., his work on the Tesla coil).
4. Funding and Financial Problems
- The tower was funded by J.P. Morgan, one of the most prominent financiers of the time, who initially believed it was primarily a communication device, not a means of transmitting free power.
- Eventually, Morgan withdrew his financial support when he realized that Tesla’s vision of free wireless power would undermine existing energy monopolies.
- Without sufficient funds, Tesla was unable to complete or fully test the tower’s potential. By 1917, the project was abandoned, and the tower was demolished for scrap.
5. Legacy and Impact
- Although the Wardenclyffe Tower was never completed, it remains an important symbol of Tesla’s visionary ideas about the future of technology.
- The concept of wireless power transmission continues to be explored, though modern technologies focus more on short-distance, high-efficiency wireless charging (e.g., inductive charging for devices).
- Tesla’s work in wireless transmission laid the groundwork for many advances in radio, radar, and even the foundations of Wi-Fi and other wireless communications.
While Tesla’s vision of global wireless electricity has not been fully realized, aspects of his work on electromagnetism and energy transmission have inspired numerous technologies that followed.